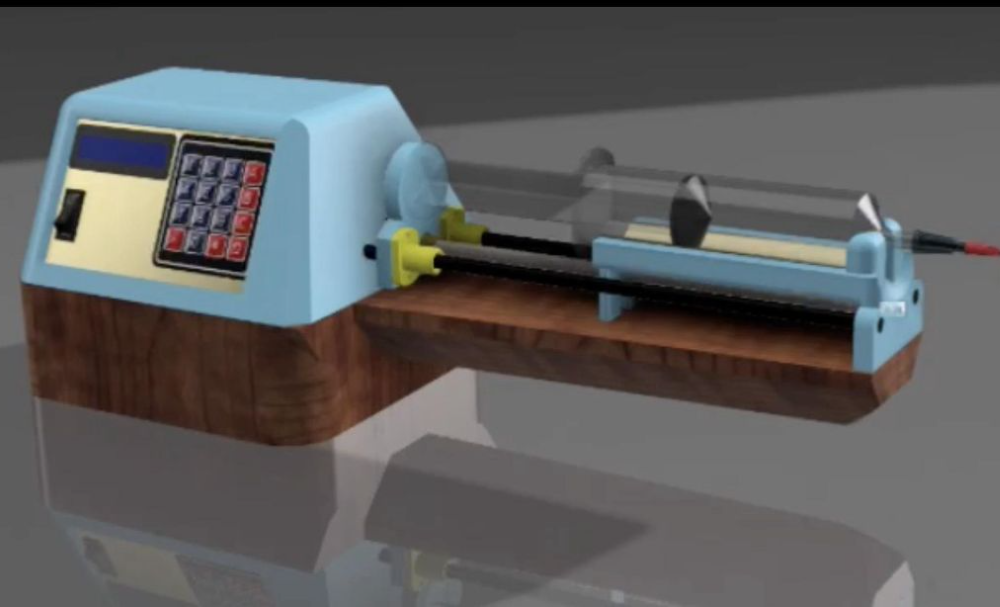
Two Biomedical Engineering students at the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Kumasi have designed a medical device to improve fluid management during surgical procedures.

The project, developed by Otema Darfour Manu and Bright Mensah, aims to reduce errors and enhance patient comfort during surgeries such as ureteroscopy and plasmapheresis.
Infusion pumps are commonly used in hospitals to deliver fluids to patients during surgery. However, many of the current systems are manually operated, which can lead to errors in fluid levels, temperature control, and timing. These issues can increase the risk of complications and patient discomfort.
To address these challenges, the students developed a two-way syringe infusion pump. The pump automatically controls both the delivery and withdrawal of fluids. It also includes a built-in warming system that maintains a consistent fluid temperature. The system uses a closed-loop control method, allowing it to adjust in real time based on the patient’s needs.
The device is particularly useful in procedures like ureteroscopy, where managing fluid pressure is critical. Improper control of pressure can damage the kidneys. With this new pump, fluid pressure is maintained at safe levels without the need for constant manual adjustments.
In plasmapheresis, where temperature control is crucial, the built-in fluid warmer ensures that the patient receives fluids at the appropriate temperature throughout the procedure. This enhances both the efficiency of the process and the patient’s comfort.
The students believe their project could help redefine surgical fluid management in hospitals across Ghana and beyond. Their next step is to conduct broader clinical tests and refine the device for use in various types of surgeries.
The project was supervised by Dr. Isaac Acquah of the Department of Computer Engineering at KNUST. The team hopes that, with additional support, their innovation can be produced at scale and implemented in hospitals to improve patient safety and procedural accuracy.
They also see potential for the device to be adapted for use in remote healthcare settings where resources are limited. The students are currently seeking partnerships to help advance the project.
| Story by Mona Lisa Frimpong(Department of Computer Engineering) | |